GIStandards
https://trbaker.github.io/GIStandards/
A machine analysis of geospatial language in US K-12 state curriculum standards
Alabama
Report date: 2021-07-08
The frequency of all keywords found in this state's standards: 52
Comparable state score: 0.191 (median: .303, SD: .324)
The frequency above is the sum of all keywords found in all of this state's four core academic standards and the state's CTE/career standards. This total count is broken down by keyword and discipline area below.
On this site, 'comparable scores' are calculated as: keywords found divided by total words in the standards document(s) - multiplied by 100,000. The comparable scores attempt to normalize data, accounting for very different sizes of curriculum guidance documentation.
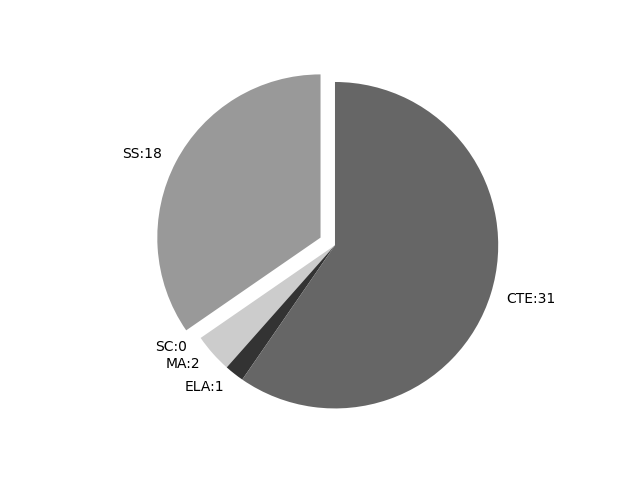
Frequencies by keyword or phrase:Frequencies by discipline area: - SS: 18
(Comp: 1.063) - SC: 0
(Comp: 0.0) - MA: 2
(Comp: 0.061) - ELA: 1
(Comp: 0.051) - CTE: 31
(Comp: 0.162)
Support files: Examples of keyword use by discipline area (and document): - CTE
- Creative Arts.pdf, page:0, position:1043
skills, and broaden opportunities for personal and professional growth. Produce Students will: 1. Create original works of art from direct observation. Organizing spatial relationships utilizing linear and atmospheric pe - 2008_General.pdf, page:74, position:1331
Navigation 4. Describe the application of publications governing electronic navigation. 5. Operate instruments that aid in electronic navigation. Examples: fathometer, radiotelephone, Global Positioning System (GPS), radar navigation 6. Utilize communicati - 2008_General.pdf, page:87, position:460
networking in an agribusiness. Positioning Systems 9. Explain the history of the global positioning system (GPS) and the geographic information system (GIS). 10. Explain ways GPS and GIS units are used in the agricultural industry. 11 - 2008_General.pdf, page:87, position:427
8. Describe advantages of computer networking in an agribusiness. Positioning Systems 9. Explain the history of the global positioning system (GPS) and the geographic information system (GIS). 10. Explain ways GPS and GIS units are used i - 2008_General.pdf, page:99, position:297
Describe computer skills used in the agricultural industry. Examples: researching electronic reference sources, managing data, analyzing data, communicating information 17. Explain uses of the geographic information system (GIS) and global positioning system (GPS) as the - 2008_General.pdf, page:99, position:327
in the agricultural industry. Examples: researching electronic reference sources, managing data, analyzing data, communicating information 17. Explain uses of the geographic information system (GIS) and global positioning system (GPS) as they rel - 2008_General.pdf, page:259, position:1034
workplace-readiness skills, and broaden opportunities for personal and professional growth. Produce Students will: 1. Create original works of art from direct observation. Organizing spatial relationships utilizing linear and atmospheric pe - 2008_General.pdf, page:436, position:967
periods for their influence on characteristics of advertising Analyzing selected illustrations for historical and cultural influences and aesthetics Analyzing layouts and designs for visual, spatial, and functional differences throughout history - 2008_General.pdf, page:440, position:523
environmental benefits 17. Describe technology used in the agriculture industry. Examples: remote sensing, robotics, global positioning systems (GPS), geographical information systems (GIS), electronic reference sources, data management - 2008_General.pdf, page:488, position:433
Association of Lighthouse Authority in the maritime industry, including aids to navigation, colors, heights, conversion scales, traffic separation schemes, correction data, notes, and terms. Global Positioning System Navigation 10. Explain fundamentals of Global P - 2008_General.pdf, page:510, position:564
problems Producing portraits for entry into competitions Evaluation 9. Evaluate various photographs for origins of specific images and ideas. Determining ways photographs differ visually, spatially, and functionally Describing how visual diffe - 2008_General.pdf, page:523, position:426
round turn and two half-hitches, sheepshank, figure eight General Navigation 10. Explain navigational aides, including lights, day shapes, whistle signals, buoys, markers, charts, and the Global Positioning System (GPS). 11. Apply navigational terms, including - 2008_General.pdf, page:535, position:56
- 2008_General.pdf, page:542, position:1312
Develop original, creative, professional, and appealing publication layouts. 5. Demonstrate effective writing skills in the development of multimedia publications. 6. Analyze images for visual, spatial, and functional differences. 7. Develop publica - Multimedia Publications.pdf, page:0, position:1312
Develop original, creative, professional, and appealing publication layouts. 5. Demonstrate effective writing skills in the development of multimedia publications. 6. Analyze images for visual, spatial, and functional differences. 7. Develop publica - Fundamentals of Agriscience-Content Standards.pdf, page:3, position:494
skills. Defining workplace issues. 15. Explore new technology in the agriculture industry and related skills found in agribusiness. Global Positioning Systems (GPS) Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Animal Science 16. Identify prom - Fundamentals of Agriscience-Content Standards.pdf, page:3, position:456
computer skills. Analyzing relationship skills. Defining workplace issues. 15. Explore new technology in the agriculture industry and related skills found in agribusiness. Global Positioning Systems (GPS) Geographic Information Systems (GIS) - Fundamentals of Agriscience-Content Standards.pdf, page:3, position:525
workplace issues. 15. Explore new technology in the agriculture industry and related skills found in agribusiness. Global Positioning Systems (GPS) Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Animal Science 16. Identify prominent - 2008 Alabama Course of Study Career and Technical Education.pdf, page:74, position:1331
Navigation 4. Describe the application of publications governing electronic navigation. 5. Operate instruments that aid in electronic navigation. Examples: fathometer, radiotelephone, Global Positioning System (GPS), radar navigation 6. Utilize communicati - 2008 Alabama Course of Study Career and Technical Education.pdf, page:87, position:460
networking in an agribusiness. Positioning Systems 9. Explain the history of the global positioning system (GPS) and the geographic information system (GIS). 10. Explain ways GPS and GIS units are used in the agricultural industry. 11 - 2008 Alabama Course of Study Career and Technical Education.pdf, page:87, position:427
8. Describe advantages of computer networking in an agribusiness. Positioning Systems 9. Explain the history of the global positioning system (GPS) and the geographic information system (GIS). 10. Explain ways GPS and GIS units are used i - 2008 Alabama Course of Study Career and Technical Education.pdf, page:99, position:297
Describe computer skills used in the agricultural industry. Examples: researching electronic reference sources, managing data, analyzing data, communicating information 17. Explain uses of the geographic information system (GIS) and global positioning system (GPS) as the - 2008 Alabama Course of Study Career and Technical Education.pdf, page:99, position:327
in the agricultural industry. Examples: researching electronic reference sources, managing data, analyzing data, communicating information 17. Explain uses of the geographic information system (GIS) and global positioning system (GPS) as they rel - 2008 Alabama Course of Study Career and Technical Education.pdf, page:259, position:1034
workplace-readiness skills, and broaden opportunities for personal and professional growth. Produce Students will: 1. Create original works of art from direct observation. Organizing spatial relationships utilizing linear and atmospheric pe - 2008 Alabama Course of Study Career and Technical Education.pdf, page:436, position:967
periods for their influence on characteristics of advertising Analyzing selected illustrations for historical and cultural influences and aesthetics Analyzing layouts and designs for visual, spatial, and functional differences throughout history - 2008 Alabama Course of Study Career and Technical Education.pdf, page:440, position:523
environmental benefits 17. Describe technology used in the agriculture industry. Examples: remote sensing, robotics, global positioning systems (GPS), geographical information systems (GIS), electronic reference sources, data management - 2008 Alabama Course of Study Career and Technical Education.pdf, page:488, position:433
Association of Lighthouse Authority in the maritime industry, including aids to navigation, colors, heights, conversion scales, traffic separation schemes, correction data, notes, and terms. Global Positioning System Navigation 10. Explain fundamentals of Global P - 2008 Alabama Course of Study Career and Technical Education.pdf, page:510, position:564
problems Producing portraits for entry into competitions Evaluation 9. Evaluate various photographs for origins of specific images and ideas. Determining ways photographs differ visually, spatially, and functionally Describing how visual diffe - 2008 Alabama Course of Study Career and Technical Education.pdf, page:523, position:426
round turn and two half-hitches, sheepshank, figure eight General Navigation 10. Explain navigational aides, including lights, day shapes, whistle signals, buoys, markers, charts, and the Global Positioning System (GPS). 11. Apply navigational terms, including - 2008 Alabama Course of Study Career and Technical Education.pdf, page:535, position:56
- 2008 Alabama Course of Study Career and Technical Education.pdf, page:542, position:1312
Develop original, creative, professional, and appealing publication layouts. 5. Demonstrate effective writing skills in the development of multimedia publications. 6. Analyze images for visual, spatial, and functional differences. 7. Develop publica
- ELA
- 2016 Revised Alabama English Language Arts Course of Study.pdf, page:44, position:1833
suspected, heard, wondered). [L.3.5c] 42. Acquire and use accurately grade-appropriate conversational, general academic, and domain-specific words and phrases, including those that signal spatial and temporal relationships (e.g., After dinner t
- MA
- 2019 Alabama Course of Study Mathematics.pdf, page:28, position:2338
time should focus on two critical areas: 1. developing a sound sense of numbers by representing and comparing numbers, using sets of objects; and 2. recognizing and describing shapes and using spatial relations. - 2019 Alabama Course of Study Mathematics.pdf, page:29, position:1962
and hexagons, presented in a variety of ways (e.g., in different sizes and orientations); identify three-dimensional shapes such as cubes, cones, cylinders, and spheres; use basic shapes and spatial reasoning to model objects in their environment t
- SS
- 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:9, position:3183
skills and concepts are addressed in all grades, students in Grade 3 and Grade 7 are involved in an intensive study of basic geography where they increase their knowledge about the physical and spatial nature of the world and about relationships betw - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:12, position:376
all grades, students in Grade 3 and Grade 7 are involved in an intensive study of geography. Through the study of geographic skills and concepts, students are able to: Describe the world in spatial terms using maps and other geographic representa - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:30, position:1686
on a gridDetermining distance between places on a map using a scaleLocating physical and cultural regions using labels,symbols, and legends on an Alabama or world mapDescribing the use of geospatial technologiesExamples: Global Positioning Syste - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:30, position:820
and interesting ways about other people, places, and cultures. This year-long study focuses on skills necessary for students to organize information about people, places, and environments in a spatial context. Although all four content strands are i - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:30, position:1722
between places on a map using a scaleLocating physical and cultural regions using labels,symbols, and legends on an Alabama or world mapDescribing the use of geospatial technologiesExamples: Global Positioning System (GPS), geographic information system (GIS) Inte - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:30, position:1786
regions using labels,symbols, and legends on an Alabama or world mapDescribing the use of geospatial technologiesExamples: Global Positioning System (GPS), geographic information system (GIS) Interpreting information on thematic mapsExamp - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:49, position:375
students study world geography using a thematic approach. They focus on Earth as the subject matter that involves people, places, and environments and learn that geography seeks meaning in spatial patterns and processes that involve asking questi - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:50, position:2485
aerial photographs, satellite images distanceŠfractional, graphic, and verbal scales directionŠlines of latitude and longitude, cardinal and intermediate directions Identifying geospatial technologies to acquire, process, and report inf - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:50, position:95
- 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:50, position:2641
and intermediate directions Identifying geospatial technologies to acquire, process, and report information from a spatial perspective Examples: Google Earth, Global Positioning System (GPS), geographic information system (GIS), satellite-remote sensing, aerial photogra - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:50, position:2607
and longitude, cardinal and intermediate directions Identifying geospatial technologies to acquire, process, and report information from a spatial perspective Examples: Google Earth, Global Positioning System (GPS), geographic information system (GIS), sate - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:50, position:2671
Identifying geospatial technologies to acquire, process, and report information from a spatial perspective Examples: Google Earth, Global Positioning System (GPS), geographic information system (GIS), satellite-remote sensing, aerial photography - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:52, position:796
human and natural processes Examples: humanŠincrease or decrease in population, land- use change in tropical forests naturalŠhurricanes, tsunamis, tornadoes, floods E G H CG 4. Evaluate spatial patterns and the demographic structure of popula - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:53, position:656
America Free Trade Agreement (DR-CAFTA), the European Union (EU), the Mercado Común del Sur (MERCOSUR), and the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) E G H CG 7. Classify spatial patterns of settlement in different regions of th - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:55, position:96
- 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:61, position:831
Examples: expansionŠillustrating the spread of Roman influence with charts, graphs, timelines, or maps transformationŠnoting reforms of Augustus, listing effects of Pax Romana Interpreting spatial distributions and patterns of the Roman Republic - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:98, position:371
nature of human geography, including how human activities help shape Earth™s surface. Students should understand population characteristics, characteristics and distribution of cultural mosaics, spatial patterns of economic interaction, processes and p - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:99, position:132
On this site, 'comparable scores' are calculated as: keywords found divided by total words in the standards document(s) - multiplied by 100,000. The comparable scores attempt to normalize data, accounting for very different sizes of curriculum guidance documentation.
(Comp: 1.063)
(Comp: 0.0)
(Comp: 0.061)
(Comp: 0.051)
(Comp: 0.162)
- Creative Arts.pdf, page:0, position:1043
skills, and broaden opportunities for personal and professional growth. Produce Students will: 1. Create original works of art from direct observation. Organizing spatial relationships utilizing linear and atmospheric pe - 2008_General.pdf, page:74, position:1331
Navigation 4. Describe the application of publications governing electronic navigation. 5. Operate instruments that aid in electronic navigation. Examples: fathometer, radiotelephone, Global Positioning System (GPS), radar navigation 6. Utilize communicati - 2008_General.pdf, page:87, position:460
networking in an agribusiness. Positioning Systems 9. Explain the history of the global positioning system (GPS) and the geographic information system (GIS). 10. Explain ways GPS and GIS units are used in the agricultural industry. 11 - 2008_General.pdf, page:87, position:427
8. Describe advantages of computer networking in an agribusiness. Positioning Systems 9. Explain the history of the global positioning system (GPS) and the geographic information system (GIS). 10. Explain ways GPS and GIS units are used i - 2008_General.pdf, page:99, position:297
Describe computer skills used in the agricultural industry. Examples: researching electronic reference sources, managing data, analyzing data, communicating information 17. Explain uses of the geographic information system (GIS) and global positioning system (GPS) as the - 2008_General.pdf, page:99, position:327
in the agricultural industry. Examples: researching electronic reference sources, managing data, analyzing data, communicating information 17. Explain uses of the geographic information system (GIS) and global positioning system (GPS) as they rel - 2008_General.pdf, page:259, position:1034
workplace-readiness skills, and broaden opportunities for personal and professional growth. Produce Students will: 1. Create original works of art from direct observation. Organizing spatial relationships utilizing linear and atmospheric pe - 2008_General.pdf, page:436, position:967
periods for their influence on characteristics of advertising Analyzing selected illustrations for historical and cultural influences and aesthetics Analyzing layouts and designs for visual, spatial, and functional differences throughout history - 2008_General.pdf, page:440, position:523
environmental benefits 17. Describe technology used in the agriculture industry. Examples: remote sensing, robotics, global positioning systems (GPS), geographical information systems (GIS), electronic reference sources, data management - 2008_General.pdf, page:488, position:433
Association of Lighthouse Authority in the maritime industry, including aids to navigation, colors, heights, conversion scales, traffic separation schemes, correction data, notes, and terms. Global Positioning System Navigation 10. Explain fundamentals of Global P - 2008_General.pdf, page:510, position:564
problems Producing portraits for entry into competitions Evaluation 9. Evaluate various photographs for origins of specific images and ideas. Determining ways photographs differ visually, spatially, and functionally Describing how visual diffe - 2008_General.pdf, page:523, position:426
round turn and two half-hitches, sheepshank, figure eight General Navigation 10. Explain navigational aides, including lights, day shapes, whistle signals, buoys, markers, charts, and the Global Positioning System (GPS). 11. Apply navigational terms, including - 2008_General.pdf, page:535, position:56
- 2008_General.pdf, page:542, position:1312
Develop original, creative, professional, and appealing publication layouts. 5. Demonstrate effective writing skills in the development of multimedia publications. 6. Analyze images for visual, spatial, and functional differences. 7. Develop publica - Multimedia Publications.pdf, page:0, position:1312
Develop original, creative, professional, and appealing publication layouts. 5. Demonstrate effective writing skills in the development of multimedia publications. 6. Analyze images for visual, spatial, and functional differences. 7. Develop publica - Fundamentals of Agriscience-Content Standards.pdf, page:3, position:494
skills. Defining workplace issues. 15. Explore new technology in the agriculture industry and related skills found in agribusiness. Global Positioning Systems (GPS) Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Animal Science 16. Identify prom - Fundamentals of Agriscience-Content Standards.pdf, page:3, position:456
computer skills. Analyzing relationship skills. Defining workplace issues. 15. Explore new technology in the agriculture industry and related skills found in agribusiness. Global Positioning Systems (GPS) Geographic Information Systems (GIS) - Fundamentals of Agriscience-Content Standards.pdf, page:3, position:525
workplace issues. 15. Explore new technology in the agriculture industry and related skills found in agribusiness. Global Positioning Systems (GPS) Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Animal Science 16. Identify prominent - 2008 Alabama Course of Study Career and Technical Education.pdf, page:74, position:1331
Navigation 4. Describe the application of publications governing electronic navigation. 5. Operate instruments that aid in electronic navigation. Examples: fathometer, radiotelephone, Global Positioning System (GPS), radar navigation 6. Utilize communicati - 2008 Alabama Course of Study Career and Technical Education.pdf, page:87, position:460
networking in an agribusiness. Positioning Systems 9. Explain the history of the global positioning system (GPS) and the geographic information system (GIS). 10. Explain ways GPS and GIS units are used in the agricultural industry. 11 - 2008 Alabama Course of Study Career and Technical Education.pdf, page:87, position:427
8. Describe advantages of computer networking in an agribusiness. Positioning Systems 9. Explain the history of the global positioning system (GPS) and the geographic information system (GIS). 10. Explain ways GPS and GIS units are used i - 2008 Alabama Course of Study Career and Technical Education.pdf, page:99, position:297
Describe computer skills used in the agricultural industry. Examples: researching electronic reference sources, managing data, analyzing data, communicating information 17. Explain uses of the geographic information system (GIS) and global positioning system (GPS) as the - 2008 Alabama Course of Study Career and Technical Education.pdf, page:99, position:327
in the agricultural industry. Examples: researching electronic reference sources, managing data, analyzing data, communicating information 17. Explain uses of the geographic information system (GIS) and global positioning system (GPS) as they rel - 2008 Alabama Course of Study Career and Technical Education.pdf, page:259, position:1034
workplace-readiness skills, and broaden opportunities for personal and professional growth. Produce Students will: 1. Create original works of art from direct observation. Organizing spatial relationships utilizing linear and atmospheric pe - 2008 Alabama Course of Study Career and Technical Education.pdf, page:436, position:967
periods for their influence on characteristics of advertising Analyzing selected illustrations for historical and cultural influences and aesthetics Analyzing layouts and designs for visual, spatial, and functional differences throughout history - 2008 Alabama Course of Study Career and Technical Education.pdf, page:440, position:523
environmental benefits 17. Describe technology used in the agriculture industry. Examples: remote sensing, robotics, global positioning systems (GPS), geographical information systems (GIS), electronic reference sources, data management - 2008 Alabama Course of Study Career and Technical Education.pdf, page:488, position:433
Association of Lighthouse Authority in the maritime industry, including aids to navigation, colors, heights, conversion scales, traffic separation schemes, correction data, notes, and terms. Global Positioning System Navigation 10. Explain fundamentals of Global P - 2008 Alabama Course of Study Career and Technical Education.pdf, page:510, position:564
problems Producing portraits for entry into competitions Evaluation 9. Evaluate various photographs for origins of specific images and ideas. Determining ways photographs differ visually, spatially, and functionally Describing how visual diffe - 2008 Alabama Course of Study Career and Technical Education.pdf, page:523, position:426
round turn and two half-hitches, sheepshank, figure eight General Navigation 10. Explain navigational aides, including lights, day shapes, whistle signals, buoys, markers, charts, and the Global Positioning System (GPS). 11. Apply navigational terms, including - 2008 Alabama Course of Study Career and Technical Education.pdf, page:535, position:56
- 2008 Alabama Course of Study Career and Technical Education.pdf, page:542, position:1312
Develop original, creative, professional, and appealing publication layouts. 5. Demonstrate effective writing skills in the development of multimedia publications. 6. Analyze images for visual, spatial, and functional differences. 7. Develop publica
- 2016 Revised Alabama English Language Arts Course of Study.pdf, page:44, position:1833
suspected, heard, wondered). [L.3.5c] 42. Acquire and use accurately grade-appropriate conversational, general academic, and domain-specific words and phrases, including those that signal spatial and temporal relationships (e.g., After dinner t
- 2019 Alabama Course of Study Mathematics.pdf, page:28, position:2338
time should focus on two critical areas: 1. developing a sound sense of numbers by representing and comparing numbers, using sets of objects; and 2. recognizing and describing shapes and using spatial relations. - 2019 Alabama Course of Study Mathematics.pdf, page:29, position:1962
and hexagons, presented in a variety of ways (e.g., in different sizes and orientations); identify three-dimensional shapes such as cubes, cones, cylinders, and spheres; use basic shapes and spatial reasoning to model objects in their environment t
- 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:9, position:3183
skills and concepts are addressed in all grades, students in Grade 3 and Grade 7 are involved in an intensive study of basic geography where they increase their knowledge about the physical and spatial nature of the world and about relationships betw - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:12, position:376
all grades, students in Grade 3 and Grade 7 are involved in an intensive study of geography. Through the study of geographic skills and concepts, students are able to: Describe the world in spatial terms using maps and other geographic representa - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:30, position:1686
on a gridDetermining distance between places on a map using a scaleLocating physical and cultural regions using labels,symbols, and legends on an Alabama or world mapDescribing the use of geospatial technologiesExamples: Global Positioning Syste - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:30, position:820
and interesting ways about other people, places, and cultures. This year-long study focuses on skills necessary for students to organize information about people, places, and environments in a spatial context. Although all four content strands are i - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:30, position:1722
between places on a map using a scaleLocating physical and cultural regions using labels,symbols, and legends on an Alabama or world mapDescribing the use of geospatial technologiesExamples: Global Positioning System (GPS), geographic information system (GIS) Inte - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:30, position:1786
regions using labels,symbols, and legends on an Alabama or world mapDescribing the use of geospatial technologiesExamples: Global Positioning System (GPS), geographic information system (GIS) Interpreting information on thematic mapsExamp - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:49, position:375
students study world geography using a thematic approach. They focus on Earth as the subject matter that involves people, places, and environments and learn that geography seeks meaning in spatial patterns and processes that involve asking questi - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:50, position:2485
aerial photographs, satellite images distanceŠfractional, graphic, and verbal scales directionŠlines of latitude and longitude, cardinal and intermediate directions Identifying geospatial technologies to acquire, process, and report inf - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:50, position:95
- 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:50, position:2641
and intermediate directions Identifying geospatial technologies to acquire, process, and report information from a spatial perspective Examples: Google Earth, Global Positioning System (GPS), geographic information system (GIS), satellite-remote sensing, aerial photogra - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:50, position:2607
and longitude, cardinal and intermediate directions Identifying geospatial technologies to acquire, process, and report information from a spatial perspective Examples: Google Earth, Global Positioning System (GPS), geographic information system (GIS), sate - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:50, position:2671
Identifying geospatial technologies to acquire, process, and report information from a spatial perspective Examples: Google Earth, Global Positioning System (GPS), geographic information system (GIS), satellite-remote sensing, aerial photography - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:52, position:796
human and natural processes Examples: humanŠincrease or decrease in population, land- use change in tropical forests naturalŠhurricanes, tsunamis, tornadoes, floods E G H CG 4. Evaluate spatial patterns and the demographic structure of popula - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:53, position:656
America Free Trade Agreement (DR-CAFTA), the European Union (EU), the Mercado Común del Sur (MERCOSUR), and the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) E G H CG 7. Classify spatial patterns of settlement in different regions of th - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:55, position:96
- 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:61, position:831
Examples: expansionŠillustrating the spread of Roman influence with charts, graphs, timelines, or maps transformationŠnoting reforms of Augustus, listing effects of Pax Romana Interpreting spatial distributions and patterns of the Roman Republic - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:98, position:371
nature of human geography, including how human activities help shape Earth™s surface. Students should understand population characteristics, characteristics and distribution of cultural mosaics, spatial patterns of economic interaction, processes and p - 2010 Alabama Social Studies Course of Study.pdf, page:99, position:132