GIStandards
https://trbaker.github.io/GIStandards/
A machine analysis of geospatial language in US K-12 state curriculum standards
Georgia
Report date: 2021-07-08
The frequency of all keywords found in this state's standards: 9
Comparable state score: 0.089 (median: .303, SD: .324)
The frequency above is the sum of all keywords found in all of this state's four core academic standards and the state's CTE/career standards. This total count is broken down by keyword and discipline area below.
On this site, 'comparable scores' are calculated as: keywords found divided by total words in the standards document(s) - multiplied by 100,000. The comparable scores attempt to normalize data, accounting for very different sizes of curriculum guidance documentation.
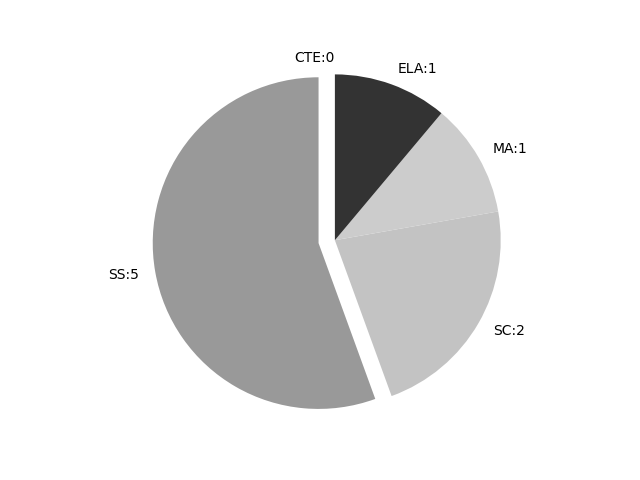
Frequencies by keyword or phrase:Frequencies by discipline area: - SS: 5
(Comp: 0.271) - SC: 2
(Comp: 0.206) - MA: 1
(Comp: 0.076) - ELA: 1
(Comp: 0.109) - CTE: 0
(Comp: 0.0)
Support files: Examples of keyword use by discipline area (and document): - ELA
- ELA-Standards-K-12-with-Glossary.pdf, page:29, position:1211
suspected, heard, wondered). ELAGSE3L6 Acquire and use accurately grade-appropriate conversational, general academic, and domain-specific vocabulary, including words and phrases that signal spatial and temporal relationships (e.g., After dinner
- MA
- Grade-K-5-Mathematics-Standards.pdf, page:1, position:1668
greater focus and coherence Mathematics experiences in early childhood settings should concentrate on (1) number (which includes whole number, operations, and relations) and (2) geometry, spatial relations, and measurement, with more mathematic
- SC
- Science-Fifth-Grade-Georgia-Standards.pdf, page:1, position:992
how technology is used to limit andor predict the impact of constructive and destructive processes. (Clarification statement: Examples could include seismological studies, flood forecasting (GIS maps), engineeringconstruction methods and mater - Earth-Systems-Georgia-Standards.pdf, page:2, position:1290
applying the principle of uniformitarianism to show the relationship between sedimentary rocks and their fossils to the environments in which they were formed. e. Construct an argument using spatial representations of Earth data that interprets ma
- SS
- Social-Studies-K-12-Georgia-Standards.pdf, page:29, position:743
a. Locate important man-made places; include the Chisholm Trail; Pittsburgh, PA; Kitty Hawk, NC; Pearl Harbor, HI; Montgomery, AL.; and Chicago, IL. SS5G2 Explain the reasons for the spatial patterns of economic activities. a. Locate pr - Social-Studies-K-12-Georgia-Standards.pdf, page:91, position:2334
Intelligence (SIGINTaka COMINT), Imagery Intelligence (IMINT), Measurement and Signature Intelligence (MASINT), Human-Source Intelligence (HUMINT), Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT), Geospatial Intelligence (GEOINT)). b. Describe other sou - Social-Studies-K-12-Georgia-Standards.pdf, page:151, position:2917
and Antarctica. Explain how these physical characteristics impact settlement patterns including, but not limited to, the Great Dividing Range and Great Victoria Desert. h. Describe the spatial distribution of natural resources, including, bu - Social-Studies-K-12-Georgia-Standards.pdf, page:153, position:183
- Social-Studies-K-12-Georgia-Standards.pdf, page:154, position:163
On this site, 'comparable scores' are calculated as: keywords found divided by total words in the standards document(s) - multiplied by 100,000. The comparable scores attempt to normalize data, accounting for very different sizes of curriculum guidance documentation.
(Comp: 0.271)
(Comp: 0.206)
(Comp: 0.076)
(Comp: 0.109)
(Comp: 0.0)
- ELA-Standards-K-12-with-Glossary.pdf, page:29, position:1211
suspected, heard, wondered). ELAGSE3L6 Acquire and use accurately grade-appropriate conversational, general academic, and domain-specific vocabulary, including words and phrases that signal spatial and temporal relationships (e.g., After dinner
- Grade-K-5-Mathematics-Standards.pdf, page:1, position:1668
greater focus and coherence Mathematics experiences in early childhood settings should concentrate on (1) number (which includes whole number, operations, and relations) and (2) geometry, spatial relations, and measurement, with more mathematic
- Science-Fifth-Grade-Georgia-Standards.pdf, page:1, position:992
how technology is used to limit andor predict the impact of constructive and destructive processes. (Clarification statement: Examples could include seismological studies, flood forecasting (GIS maps), engineeringconstruction methods and mater - Earth-Systems-Georgia-Standards.pdf, page:2, position:1290
applying the principle of uniformitarianism to show the relationship between sedimentary rocks and their fossils to the environments in which they were formed. e. Construct an argument using spatial representations of Earth data that interprets ma
- Social-Studies-K-12-Georgia-Standards.pdf, page:29, position:743
a. Locate important man-made places; include the Chisholm Trail; Pittsburgh, PA; Kitty Hawk, NC; Pearl Harbor, HI; Montgomery, AL.; and Chicago, IL. SS5G2 Explain the reasons for the spatial patterns of economic activities. a. Locate pr - Social-Studies-K-12-Georgia-Standards.pdf, page:91, position:2334
Intelligence (SIGINTaka COMINT), Imagery Intelligence (IMINT), Measurement and Signature Intelligence (MASINT), Human-Source Intelligence (HUMINT), Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT), Geospatial Intelligence (GEOINT)). b. Describe other sou - Social-Studies-K-12-Georgia-Standards.pdf, page:151, position:2917
and Antarctica. Explain how these physical characteristics impact settlement patterns including, but not limited to, the Great Dividing Range and Great Victoria Desert. h. Describe the spatial distribution of natural resources, including, bu - Social-Studies-K-12-Georgia-Standards.pdf, page:153, position:183
- Social-Studies-K-12-Georgia-Standards.pdf, page:154, position:163