GIStandards
https://trbaker.github.io/GIStandards/
A machine analysis of geospatial language in US K-12 state curriculum standards
Hawaii
Report date: 2021-07-08
The frequency of all keywords found in this state's standards: 18
Comparable state score: 0.625 (median: .303, SD: .324)
The frequency above is the sum of all keywords found in all of this state's four core academic standards and the state's CTE/career standards. This total count is broken down by keyword and discipline area below.
On this site, 'comparable scores' are calculated as: keywords found divided by total words in the standards document(s) - multiplied by 100,000. The comparable scores attempt to normalize data, accounting for very different sizes of curriculum guidance documentation.
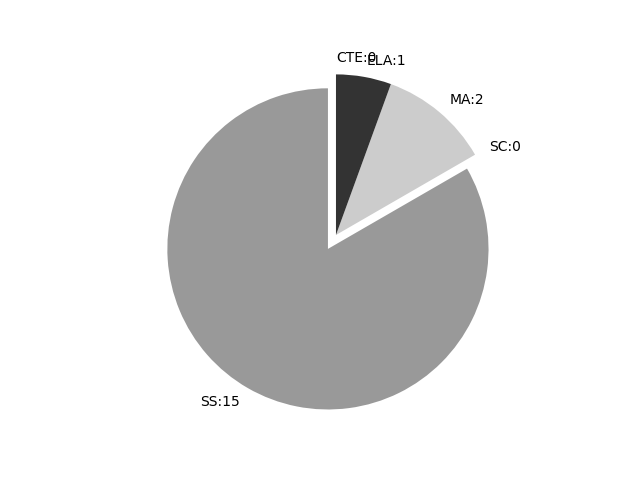
Frequencies by keyword or phrase:Frequencies by discipline area: - SS: 15
(Comp: 2.193) - SC: 0
(Comp: 0.0) - MA: 2
(Comp: 0.188) - ELA: 1
(Comp: 0.18) - CTE: 0
(Comp: None)
Support files: Examples of keyword use by discipline area (and document): - ELA
- ADA_CC_ELAStandards.pdf, page:27, position:4345
to better understand each of the words.6.Acquire and use accurately grade-appropriate conversational, general academic, and domain- speciÞc words and phrases, including those that signal spatial and temporal relationships (e.g., After dinner
- MA
- ADA_CC_MathStandards.pdf, page:1, position:565
greater focus and coherenceMathematics experiences in early childhood settings should concentrate on(1) number (which includes whole number, operations, and relations) and (2) geometry, spatial relations, and measurement, with more mathema - ADA_CC_MathStandards.pdf, page:8, position:309
combined sets, or counting the number of objects that remain in a set after some are taken away.Students describe their physical world using geometric ideas (e.g., shape, orientation, spatial relations) and vocabulary. They identify, nam
- SS
- HCSSSModHistHawaii.pdf, page:4, position:419
Standard Sample ContentConcepts The student demonstrates an understanding of Therefore, the student is able to Geography Anchor Standard 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns is Geopolitical Position Conte - HCSSSgr8USHist.pdf, page:4, position:873
cotton production, fur trade, gold rush, Homestead Act, population growth, railroads, steamboats, technological advances Geography Anchor Standard 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns Acquisition of Western Territory - HCSSSgr4.pdf, page:3, position:1040
hotspot Relative Location: distance and direction from continental US, Australia, South America, Japan, and China Geography Anchor Standard 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns Human Distribution Content Stand - HCSSSgr4.pdf, page:5, position:437
Standard Sample ContentConcepts The student demonstrates an understanding of Therefore, the student is able to Geography Anchor Standard 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns Hawaiian and Other Polynesian Cult - HCSSSgr3.pdf, page:4, position:1043
why people migrate and where they settle Push and Pull Factors: disasters, economics, human rights, religion Geography Anchor Standard 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns Interdependence Content Standard SS - HCSSSgr3.pdf, page:5, position:1321
or stores, climate change, housing developments Political Impacts: passage of laws for nature conservation Geography Anchor Standards 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns Disasters Content Standards SS.3.4 - HCSSSgr2.pdf, page:4, position:928
high cost of food, higher cost of housing, higher gas and electricity costs, higher wages, need to hire non-local labor Geography Anchor Standard 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns Interactions and Impact Content St - HCSSSgr6WorldHist.pdf, page:8, position:413
Standard Sample ContentConcepts The student demonstrates an understanding of Therefore, the student is able to Geography Anchor Standard 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns Characteristics of Mesoamerican E - HCSSSdemocracy.pdf, page:5, position:1408
Social Services Provided by Government: educational grants and loans, Medicare and Medicaid, Social Security, Geography Anchor Standard 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns The Global Role of the United State - HCSSSWorldHistCulture.pdf, page:2, position:1861
System: cotton, slave labor, sugar Human Consequences: African warfare, Door of No Return, European development Geography Anchor Standard 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns Columbian Exchange and Consequences - HCSSSWorldHistCulture.pdf, page:3, position:973
Emperor Kangxi, new law and tax codes Tokugawa Japan: daimyo, feudalism, samurai retainers, shogun, Tokugawa leyasu Geography Anchor Standard 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns European Expansion and Trade Cont - HCSSSWorldHistCulture.pdf, page:5, position:961
for steel, new markets, oil, rubber Military and Political Motivations: military power and bases, national security Geography Anchor Standard 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns Imperialist Methods Content Stan - HCSSSUShistgov.pdf, page:2, position:447
Standard Sample ContentConcepts The student demonstrates an understanding of Therefore, the student is able to Geography Anchor Standard 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns Cause and Effects of Migration Co - HCSSSUShistgov.pdf, page:5, position:864
and Policies: Open Door Policy, Spanish-American War, Hawaii annexation, Panama Canal, Roosevelt Corollary Geography Anchor Standard 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns Effects of U.S. Foreign Policy C - HCSSSUShistgov.pdf, page:14, position:823
reform, racial division Responses: education reform, health care restructuring, new social movements, tax policy Geography Anchor Standard 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns Global Challenges Content Standa
On this site, 'comparable scores' are calculated as: keywords found divided by total words in the standards document(s) - multiplied by 100,000. The comparable scores attempt to normalize data, accounting for very different sizes of curriculum guidance documentation.
(Comp: 2.193)
(Comp: 0.0)
(Comp: 0.188)
(Comp: 0.18)
(Comp: None)
- ADA_CC_ELAStandards.pdf, page:27, position:4345
to better understand each of the words.6.Acquire and use accurately grade-appropriate conversational, general academic, and domain- speciÞc words and phrases, including those that signal spatial and temporal relationships (e.g., After dinner
- ADA_CC_MathStandards.pdf, page:1, position:565
greater focus and coherenceMathematics experiences in early childhood settings should concentrate on(1) number (which includes whole number, operations, and relations) and (2) geometry, spatial relations, and measurement, with more mathema - ADA_CC_MathStandards.pdf, page:8, position:309
combined sets, or counting the number of objects that remain in a set after some are taken away.Students describe their physical world using geometric ideas (e.g., shape, orientation, spatial relations) and vocabulary. They identify, nam
- HCSSSModHistHawaii.pdf, page:4, position:419
Standard Sample ContentConcepts The student demonstrates an understanding of Therefore, the student is able to Geography Anchor Standard 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns is Geopolitical Position Conte - HCSSSgr8USHist.pdf, page:4, position:873
cotton production, fur trade, gold rush, Homestead Act, population growth, railroads, steamboats, technological advances Geography Anchor Standard 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns Acquisition of Western Territory - HCSSSgr4.pdf, page:3, position:1040
hotspot Relative Location: distance and direction from continental US, Australia, South America, Japan, and China Geography Anchor Standard 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns Human Distribution Content Stand - HCSSSgr4.pdf, page:5, position:437
Standard Sample ContentConcepts The student demonstrates an understanding of Therefore, the student is able to Geography Anchor Standard 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns Hawaiian and Other Polynesian Cult - HCSSSgr3.pdf, page:4, position:1043
why people migrate and where they settle Push and Pull Factors: disasters, economics, human rights, religion Geography Anchor Standard 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns Interdependence Content Standard SS - HCSSSgr3.pdf, page:5, position:1321
or stores, climate change, housing developments Political Impacts: passage of laws for nature conservation Geography Anchor Standards 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns Disasters Content Standards SS.3.4 - HCSSSgr2.pdf, page:4, position:928
high cost of food, higher cost of housing, higher gas and electricity costs, higher wages, need to hire non-local labor Geography Anchor Standard 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns Interactions and Impact Content St - HCSSSgr6WorldHist.pdf, page:8, position:413
Standard Sample ContentConcepts The student demonstrates an understanding of Therefore, the student is able to Geography Anchor Standard 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns Characteristics of Mesoamerican E - HCSSSdemocracy.pdf, page:5, position:1408
Social Services Provided by Government: educational grants and loans, Medicare and Medicaid, Social Security, Geography Anchor Standard 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns The Global Role of the United State - HCSSSWorldHistCulture.pdf, page:2, position:1861
System: cotton, slave labor, sugar Human Consequences: African warfare, Door of No Return, European development Geography Anchor Standard 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns Columbian Exchange and Consequences - HCSSSWorldHistCulture.pdf, page:3, position:973
Emperor Kangxi, new law and tax codes Tokugawa Japan: daimyo, feudalism, samurai retainers, shogun, Tokugawa leyasu Geography Anchor Standard 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns European Expansion and Trade Cont - HCSSSWorldHistCulture.pdf, page:5, position:961
for steel, new markets, oil, rubber Military and Political Motivations: military power and bases, national security Geography Anchor Standard 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns Imperialist Methods Content Stan - HCSSSUShistgov.pdf, page:2, position:447
Standard Sample ContentConcepts The student demonstrates an understanding of Therefore, the student is able to Geography Anchor Standard 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns Cause and Effects of Migration Co - HCSSSUShistgov.pdf, page:5, position:864
and Policies: Open Door Policy, Spanish-American War, Hawaii annexation, Panama Canal, Roosevelt Corollary Geography Anchor Standard 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns Effects of U.S. Foreign Policy C - HCSSSUShistgov.pdf, page:14, position:823
reform, racial division Responses: education reform, health care restructuring, new social movements, tax policy Geography Anchor Standard 16 Global Interconnections: Changing Spatial Patterns Global Challenges Content Standa