GIStandards
https://trbaker.github.io/GIStandards/
A machine analysis of geospatial language in US K-12 state curriculum standards
Kentucky
Report date: 2021-07-08
The frequency of all keywords found in this state's standards: 31
Comparable state score: 0.323 (median: .303, SD: .324)
The frequency above is the sum of all keywords found in all of this state's four core academic standards and the state's CTE/career standards. This total count is broken down by keyword and discipline area below.
On this site, 'comparable scores' are calculated as: keywords found divided by total words in the standards document(s) - multiplied by 100,000. The comparable scores attempt to normalize data, accounting for very different sizes of curriculum guidance documentation.
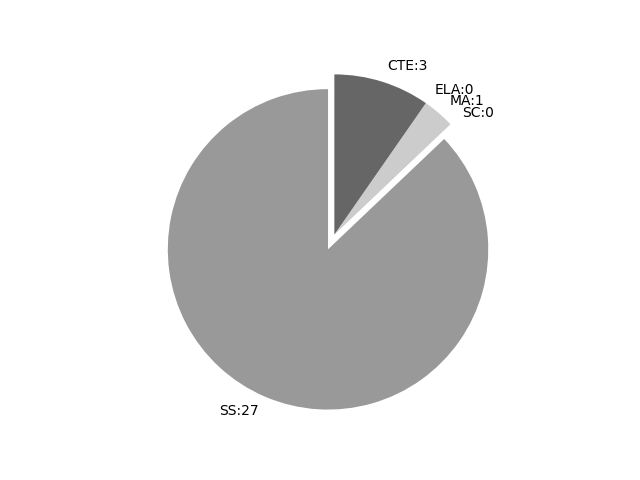
Frequencies by keyword or phrase:Frequencies by discipline area: - SS: 27
(Comp: 1.415) - SC: 0
(Comp: 0.0) - MA: 1
(Comp: 0.043) - ELA: 0
(Comp: 0.0) - CTE: 3
(Comp: 0.125)
Support files: Examples of keyword use by discipline area (and document): - CTE
- AgPower-PathStnd.pdf, page:8, position:1198
webDVD based service information, software diagnostics) OE2 Demonstrate electricity principles via the use of volt and amp meters and continuity testers OE3 Evaluate concepts and principles of geospatial technologies OE4 Describe equipment and process - EnvSciNatRes-PathStnd.pdf, page:8, position:481
calculate actual distance, and determine the elevations of points OE2 Locate natural resources using a land survey and geographic coordinate system OE3 Employ Global Positioning System and Geographic Information Systems technologies to inventory features in natural r - EnvSciNatRes-PathStnd.pdf, page:8, position:451
to identify directions, features, calculate actual distance, and determine the elevations of points OE2 Locate natural resources using a land survey and geographic coordinate system OE3 Employ Global Positioning System and Geographic Information Systems technologies t
- MA
- Kentucky_Academic_Standards_Mathematics.pdf, page:15, position:2157
remain in a set after some are taken away. 2. In the Geometry and Measurement and Data domains, students will: describe their physical world using geometric ideas (e.g., shape, orientation, spatial relations) and appropriate vocabulary; identi
- SS
- Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:17, position:2101
Geographic reasoning refers to understanding the location, scale, patterns and trends of the geographic and temporal relationships among data, phenomena and issues. Creating maps and using geospatial technologies requires a process of answering geo - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:17, position:852
Kentucky G: Migration and Movement The size, composition, distribution and movement of human populations are fundamental and active without asking and answering questions about the spatial patterns of human population. G: Human I - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:97, position:1625
and resulted in the growth of markets and changes within them, for example, the shift from bartering to coin-based economies. 6.G.GR.1 Use maps and other geographic representations, geospatial technologies, and spatial thinking to determi - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:100, position:2045
and Classical Empires impacted the environment, both positively and negatively, between 3500 BCE-600 CE. G: Geographic Reasoning 6.G.GR.1 Use maps and other geographic representations, geospatial technologies, and spatial thinking to determi - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:107, position:2299
deforestation to create the charcoal used in smelting furnaces in places like Rome and Han Dynasty China. G: Geographic Reasoning 6.G.GR.1 Use maps and other geographic representations, geospatial technologies, and spatial thinking to deter - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:107, position:2330
used in smelting furnaces in places like Rome and Han Dynasty China. G: Geographic Reasoning 6.G.GR.1 Use maps and other geographic representations, geospatial technologies, and spatial thinking to determine similarities and differe - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:114, position:2247
spatial organization of people, places and environments found in the societies and empires of Afro-Eurasia and the Americas between 600-1600. Use maps and other geographic representations, geospatial technologies, and spatial thinking to interpr - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:121, position:635
of people, places and environments found in the societies and empires of Afro-Eurasia and the Americas between 600-1600. 7.G.GR.2 Use maps and other geographic representations, geospatial technologies, and spatial thinking to interpr - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:121, position:414
Statement which negatively impacted food supply, sparking innovations like the three-field system as well as further migration to new lands. G: Geographic Reasoning 7.G.GR.1 Analyze the spatial organization of people, places and environment - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:128, position:1038
with their environments in the United States from the Colonial Era to Reconstruction from 1600-1877. G: Geographic Reasoning 8.G.GR.1 Use maps and other geographic representations, geospatial technologies, and spatial thinking to analyze - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:128, position:1069
the United States from the Colonial Era to Reconstruction from 1600-1877. G: Geographic Reasoning 8.G.GR.1 Use maps and other geographic representations, geospatial technologies, and spatial thinking to analyze settlement patterns in the U - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:135, position:1362
the invention of the Cotton Gin led to an increase in demand for slave labor and an increase in production. G: Geographic Reasoning 8.G.GR.1 Use maps and other geographic representations, geospatial technologies, and spatial thinking to anal - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:135, position:1394
led to an increase in demand for slave labor and an increase in production. G: Geographic Reasoning 8.G.GR.1 Use maps and other geographic representations, geospatial technologies, and spatial thinking to analyze settlement patterns in the - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:138, position:2764
global. Within the geography standards, the interplay between human systems and the natural environment is evident. The standards promote the use of a variety of geographic methods and tools for spatial analysis. By developing inquiry skills in geograp - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:145, position:370
global. Within the geography standards, the interplay between human systems and the natural environment is evident. The standards promote the use of a variety of geographic methods and tools for spatial analysis. By developing inquiry skills in geograp - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:197, position:641
and Classical Empires impacted the environment, both positively and negatively, between 3500 BCE-600 CE. G: Geographic Reasoning 6.G.GR.1 Use maps and other geographic representations, geospatial technologies, and spatial thinking to determ - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:197, position:672
the environment, both positively and negatively, between 3500 BCE-600 CE. G: Geographic Reasoning 6.G.GR.1 Use maps and other geographic representations, geospatial technologies, and spatial thinking to determine similarities and differe - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:198, position:827
with their environments in the United States from the Colonial Era to Reconstruction from 1600-1877. G: Geographic Reasoning 8.G.GR.1 Use maps and other geographic representations, geospatial technologies, and spatial thinking to analyze - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:198, position:1339
HS.G.MM.1 Analyze how cultural, economic and environmental factors contribute to migration patterns and population distribution at multiple scales. HS.G.MM.2 Evaluate reasons for the spatial distribution of human populations at different sc - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:200, position:200
201 Geography Progression: Migration and Movement Causes and consequences of migration are influenced by culturalcannot be fully understood without asking and answering questions about the spatial patterns of human population. Within this docum - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:201, position:300
HS.G.MM.1 Analyze how cultural, economic and environmental factors contribute to migration patterns and population distribution at multiple scales. HS.G.MM.2 Evaluate reasons for the spatial distribution of human - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:202, position:176
- Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:204, position:327
across broad regions. Culture influences the locations and types of interactions re in constant interaction and have reciprocal influences among them. These interactions result in a variety of spatial patterns that require careful observation, invest - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:206, position:246
Geographic reasoning refers to understanding the location, scale, patterns and trends of the geographic and temporal relationships among data, phenomena and issues. Creating maps and using geospatial technologies requires a process of answering geog - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:206, position:1905
and regions and their human and environmental characteristics. Grade 6 G: Geographic Reasoning 6.G.GR.1 Use maps and other geographic representations, geospatial technologies, and spatial thinking to determine similarities and differenc - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:207, position:158
- Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:207, position:190
On this site, 'comparable scores' are calculated as: keywords found divided by total words in the standards document(s) - multiplied by 100,000. The comparable scores attempt to normalize data, accounting for very different sizes of curriculum guidance documentation.
(Comp: 1.415)
(Comp: 0.0)
(Comp: 0.043)
(Comp: 0.0)
(Comp: 0.125)
- AgPower-PathStnd.pdf, page:8, position:1198
webDVD based service information, software diagnostics) OE2 Demonstrate electricity principles via the use of volt and amp meters and continuity testers OE3 Evaluate concepts and principles of geospatial technologies OE4 Describe equipment and process - EnvSciNatRes-PathStnd.pdf, page:8, position:481
calculate actual distance, and determine the elevations of points OE2 Locate natural resources using a land survey and geographic coordinate system OE3 Employ Global Positioning System and Geographic Information Systems technologies to inventory features in natural r - EnvSciNatRes-PathStnd.pdf, page:8, position:451
to identify directions, features, calculate actual distance, and determine the elevations of points OE2 Locate natural resources using a land survey and geographic coordinate system OE3 Employ Global Positioning System and Geographic Information Systems technologies t
- Kentucky_Academic_Standards_Mathematics.pdf, page:15, position:2157
remain in a set after some are taken away. 2. In the Geometry and Measurement and Data domains, students will: describe their physical world using geometric ideas (e.g., shape, orientation, spatial relations) and appropriate vocabulary; identi
- Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:17, position:2101
Geographic reasoning refers to understanding the location, scale, patterns and trends of the geographic and temporal relationships among data, phenomena and issues. Creating maps and using geospatial technologies requires a process of answering geo - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:17, position:852
Kentucky G: Migration and Movement The size, composition, distribution and movement of human populations are fundamental and active without asking and answering questions about the spatial patterns of human population. G: Human I - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:97, position:1625
and resulted in the growth of markets and changes within them, for example, the shift from bartering to coin-based economies. 6.G.GR.1 Use maps and other geographic representations, geospatial technologies, and spatial thinking to determi - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:100, position:2045
and Classical Empires impacted the environment, both positively and negatively, between 3500 BCE-600 CE. G: Geographic Reasoning 6.G.GR.1 Use maps and other geographic representations, geospatial technologies, and spatial thinking to determi - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:107, position:2299
deforestation to create the charcoal used in smelting furnaces in places like Rome and Han Dynasty China. G: Geographic Reasoning 6.G.GR.1 Use maps and other geographic representations, geospatial technologies, and spatial thinking to deter - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:107, position:2330
used in smelting furnaces in places like Rome and Han Dynasty China. G: Geographic Reasoning 6.G.GR.1 Use maps and other geographic representations, geospatial technologies, and spatial thinking to determine similarities and differe - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:114, position:2247
spatial organization of people, places and environments found in the societies and empires of Afro-Eurasia and the Americas between 600-1600. Use maps and other geographic representations, geospatial technologies, and spatial thinking to interpr - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:121, position:635
of people, places and environments found in the societies and empires of Afro-Eurasia and the Americas between 600-1600. 7.G.GR.2 Use maps and other geographic representations, geospatial technologies, and spatial thinking to interpr - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:121, position:414
Statement which negatively impacted food supply, sparking innovations like the three-field system as well as further migration to new lands. G: Geographic Reasoning 7.G.GR.1 Analyze the spatial organization of people, places and environment - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:128, position:1038
with their environments in the United States from the Colonial Era to Reconstruction from 1600-1877. G: Geographic Reasoning 8.G.GR.1 Use maps and other geographic representations, geospatial technologies, and spatial thinking to analyze - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:128, position:1069
the United States from the Colonial Era to Reconstruction from 1600-1877. G: Geographic Reasoning 8.G.GR.1 Use maps and other geographic representations, geospatial technologies, and spatial thinking to analyze settlement patterns in the U - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:135, position:1362
the invention of the Cotton Gin led to an increase in demand for slave labor and an increase in production. G: Geographic Reasoning 8.G.GR.1 Use maps and other geographic representations, geospatial technologies, and spatial thinking to anal - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:135, position:1394
led to an increase in demand for slave labor and an increase in production. G: Geographic Reasoning 8.G.GR.1 Use maps and other geographic representations, geospatial technologies, and spatial thinking to analyze settlement patterns in the - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:138, position:2764
global. Within the geography standards, the interplay between human systems and the natural environment is evident. The standards promote the use of a variety of geographic methods and tools for spatial analysis. By developing inquiry skills in geograp - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:145, position:370
global. Within the geography standards, the interplay between human systems and the natural environment is evident. The standards promote the use of a variety of geographic methods and tools for spatial analysis. By developing inquiry skills in geograp - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:197, position:641
and Classical Empires impacted the environment, both positively and negatively, between 3500 BCE-600 CE. G: Geographic Reasoning 6.G.GR.1 Use maps and other geographic representations, geospatial technologies, and spatial thinking to determ - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:197, position:672
the environment, both positively and negatively, between 3500 BCE-600 CE. G: Geographic Reasoning 6.G.GR.1 Use maps and other geographic representations, geospatial technologies, and spatial thinking to determine similarities and differe - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:198, position:827
with their environments in the United States from the Colonial Era to Reconstruction from 1600-1877. G: Geographic Reasoning 8.G.GR.1 Use maps and other geographic representations, geospatial technologies, and spatial thinking to analyze - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:198, position:1339
HS.G.MM.1 Analyze how cultural, economic and environmental factors contribute to migration patterns and population distribution at multiple scales. HS.G.MM.2 Evaluate reasons for the spatial distribution of human populations at different sc - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:200, position:200
201 Geography Progression: Migration and Movement Causes and consequences of migration are influenced by culturalcannot be fully understood without asking and answering questions about the spatial patterns of human population. Within this docum - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:201, position:300
HS.G.MM.1 Analyze how cultural, economic and environmental factors contribute to migration patterns and population distribution at multiple scales. HS.G.MM.2 Evaluate reasons for the spatial distribution of human - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:202, position:176
- Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:204, position:327
across broad regions. Culture influences the locations and types of interactions re in constant interaction and have reciprocal influences among them. These interactions result in a variety of spatial patterns that require careful observation, invest - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:206, position:246
Geographic reasoning refers to understanding the location, scale, patterns and trends of the geographic and temporal relationships among data, phenomena and issues. Creating maps and using geospatial technologies requires a process of answering geog - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:206, position:1905
and regions and their human and environmental characteristics. Grade 6 G: Geographic Reasoning 6.G.GR.1 Use maps and other geographic representations, geospatial technologies, and spatial thinking to determine similarities and differenc - Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:207, position:158
- Kentucky_Academic_Standards_for_Social_Studies_2019.pdf, page:207, position:190