GIStandards
https://trbaker.github.io/GIStandards/
A machine analysis of geospatial language in US K-12 state curriculum standards
Minnesota
Report date: 2021-07-08
The frequency of all keywords found in this state's standards: 72
Comparable state score: 1.06 (median: .303, SD: .324)
The frequency above is the sum of all keywords found in all of this state's four core academic standards and the state's CTE/career standards. This total count is broken down by keyword and discipline area below.
On this site, 'comparable scores' are calculated as: keywords found divided by total words in the standards document(s) - multiplied by 100,000. The comparable scores attempt to normalize data, accounting for very different sizes of curriculum guidance documentation.
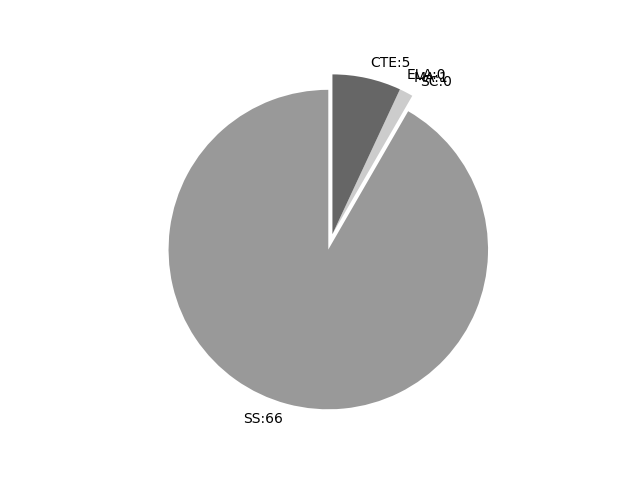
Frequencies by keyword or phrase:Frequencies by discipline area: - SS: 66
(Comp: 5.549) - SC: 0
(Comp: 0.0) - MA: 1
(Comp: 0.174) - ELA: 0
(Comp: 0.0) - CTE: 5
(Comp: 0.135)
Support files: Examples of keyword use by discipline area (and document): - CTE
- Natural Resource and Environmental Service Systems Pathway.pdf, page:12, position:2314
tools, and technologies (e.g., spread of invasive species, movement of wildlife populations, changes to biodiversity of edge of habitat versus interior, etc.). NRES.03.02.02.a. Summarize how GIS can be used to manage, conserve, improve and e - Natural Resource and Environmental Service Systems Pathway.pdf, page:28, position:1322
Demonstrate surveying and cartographic skills to make site measurements in order to address concerns and needs within an ESS situation. NRES.09.01.02.a. Research the methods in which GIS can be used in ESS (e.g., tracing of point pol - Power Structural and Technical Systems Pathway.pdf, page:12, position:833
electrical motor. PST.04.03.07.c. Plan and wire electrical circuits (i.e., single pole switch, three-way switch, duplex outlet, etc.). Minnesota Framework: MN.PST.05. Use control, monitoring, geospatial and other technologies in AFNR power, structural - Power Structural and Technical Systems Pathway.pdf, page:14, position:1441
MN.PST.05.03 Intermediate Course Benchmarks MN.PST.05.03 Advanced Course Benchmarks PST.05.03.01.a. Research and summarize the impact of utilizing geospatial technologies (i.e., GPS, GIS, remote sensing, telematics, etc.) in AFNR sys - Power Structural and Technical Systems Pathway.pdf, page:14, position:186
- MA
- Minnesota K-12 Academic Standards in Mathematics 2007 edits May 2022.pdf, page:3, position:989
as shape, size, color and thickness. K Geometry & Measurement Recognize and sort basic two- and three-dimensional shapes; use them to model real-world objects. K.3.1.3 Use basic shapes and spatial reasoning to model objects in the real-world. F
- SS
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:4, position:1377
local environments and current times to faraway places and distant times. In addition to learning key concepts, students begin to apply essential disciplinary skills including civics skills, geospatial skills, economic reasoning and historical inquiry - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:5, position:1354
history and government from 1800 to contemporary times. Social studies in the middle grades culminates in the interdisciplinary learning experiences of Global Studies in grade 8. Students apply spatial and chronological perspectives as they study the - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:13, position:128
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:13, position:204
Substrands and Standards Substrand 1: Geospatial Skills Standard 1 People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report information within a spatial context. Standard 2 Geographic inquiry is a p - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:13, position:53
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:18, position:1847
(actions or activities). For example: GoodsŠapple, shirt, toy. ServicesŠhaircut, bus ride, bicycle repair. K 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report info - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:18, position:1923
bus ride, bicycle repair. K 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report information within a spatial context. 0.3.1.1.1 Describe spatial information - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:18, position:1781
between goods (objects that can be seen or touched) and services (actions or activities). For example: GoodsŠapple, shirt, toy. ServicesŠhaircut, bus ride, bicycle repair. K 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:19, position:158
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:19, position:236
that... Code Benchmark K 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report information within a spatial context. 0.3.1.1.2 Describe a map and a globe a - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:19, position:92
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:23, position:158
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:23, position:300
Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report information within a spatial context. 1.3.1.1.1 Create sketch maps to illustrate spatial information about familiar places; describe spat - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:23, position:92
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:23, position:405
report information within a spatial context. 1.3.1.1.1 Create sketch maps to illustrate spatial information about familiar places; describe spatial information found on maps. For example: Spatial informationŠcities, roads, boundaries, bodies - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:27, position:1537
shells used in ancient China, metal coins used in Anatolia (Turkey) in 500 BCE. 2 3. Geography 1. Geospatial SkillsŠThe World in Spatial Terms 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report info - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:27, position:1613
BCE. 2 3. Geography 1. Geospatial SkillsŠThe World in Spatial Terms 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report information within a spatial context. 2.3.1.1.1 Create sketch maps to illust - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:27, position:1443
furs used in Minnesota territory in the early 1800s; salt used in the Roman Empire; cowry shells used in ancient China, metal coins used in Anatolia (Turkey) in 500 BCE. 2 3. Geography 1. Geospatial SkillsŠThe World in Spatial Terms 1. People us - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:27, position:1474
in the early 1800s; salt used in the Roman Empire; cowry shells used in ancient China, metal coins used in Anatolia (Turkey) in 500 BCE. 2 3. Geography 1. Geospatial SkillsŠThe World in Spatial Terms 1. People use geographic representations - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:28, position:187
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:28, position:263
2 3. Geography 1. Geospatial SkillsŠThe World in Spatial Terms 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report information within a spatial context. 2.3.1.1.3 Use maps, photos or other ge - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:28, position:92
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:28, position:124
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:32, position:2129
workers, and machines) required to produce 4.the refrigerators. 3 y 1. People use geographic representations and 3.3.1.1.1 Use maps and concepts of location (relative location aphptialgeospatial technologies to acquire, process and words and c - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:32, position:2266
maps and concepts of location (relative location aphptialgeospatial technologies to acquire, process and words and cardinal and intermediate directions) to Skills report information within a spatial context. describe places in one™s community, the - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:33, position:380
of the United States." Description using intermediate directionsŠfiHawaii is southwest of the continental United States.fl 3 eogaphyr ial Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report in - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:33, position:458
is southwest of the continental United States.fl 3 eogaphyr ial Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report information within a spatial context. 3.3.1.1.2 Create and interpret simple - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:33, position:870
information. 3. G1. GeospatFor example: Global placesŠcountry, continent, ocean. "TODALS" map basicsŠtitle, orientation, date, author, legend (key), and scale. Local placesŠcity, village. Spatial informationŠcities, roads, boundaries, bodies - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:35, position:600
and space. For example: Calendar systemsŠSun dial, Chinese, Hindu, Mayan or Aztec, Hebrew and Islamic calendars, Dakota or Anishinaabe seasonal cycles. Visual representations of location and spatial informationŠChinese "Jingban Tianwen Quantu" m - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:39, position:158
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:39, position:235
Understand that... Code Benchmark 4 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report information within a spatial context. 4.3.1.1.1 Create and use various kind - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:39, position:92
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:40, position:352
people ask geographic questions and gather, organize and analyze information to solve problems and plan for the future. 4.3.1.2.2 Use photographs or satellite-produced images to interpret spatial information about the United States, and also C - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:40, position:92
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:47, position:157
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:47, position:233
Understand that... Code Benchmark 5 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report information within a spatial context. 5.3.1.1.1 Create and use various kinds - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:47, position:92
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:58, position:960
Commission), wildlife preservation (Department of Natural Resources); anti-trust laws to promote competition. 6 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report info - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:58, position:1260
Create and use various kinds of maps, including overlaying thematic maps, of places in Minnesota; incorporate the fiTODALSSfl map basics, as well as points, lines and colored areas to display spatial information. For example: fiTODALSSfl map basics - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:58, position:894
oversight (Securities and Exchange Commission, Federal Trade Commission), wildlife preservation (Department of Natural Resources); anti-trust laws to promote competition. 6 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:58, position:1387
map basics, as well as points, lines and colored areas to display spatial information. For example: fiTODALSSfl map basicsŠtitle, orientation, date, author, legend key, source, and scale. Spatial informationŠcities, roads, boundaries, bodies - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:70, position:920
(Facebook). Undesirable effectsŠPonzi schemes; exploitation of people, the environment, natural resources. 7 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report info - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:70, position:996
environment, natural resources. 7 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report information within a spatial context. 7.3.1.1.1 Create and use various kinds - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:70, position:855
Winfrey, Bill Gates (Microsoft), Martha Stewart, Mark Zuckerberg (Facebook). Undesirable effectsŠPonzi schemes; exploitation of people, the environment, natural resources. 7 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:70, position:1354
map basics, as well as points, lines and colored areas to display spatial information. For example: fiTODALSSfl map basicsŠtitle, orientation, date, author, legend key, source, and scale. Spatial informationŠcities, roads, boundaries, bodies - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:80, position:2267
and Ideas Economic Development and Trade Population and Migration Human Interaction with the Environment Skills such as civic participation, economic reasoning, geographic inquiry and geospatial technology, and historical inquiry Page 81 of - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:83, position:1664
analyze geographic information from a variety of print and electronic sources to investigate places or answer specific geographic questions; provide rationale for its use. For example: SourcesŠGeographic Information Systems (GIS), online atlases and databases, Google Ear - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:83, position:1345
pizzas and Country B specialized in producing rugs and they traded at a rate of one rug for one pizza. 8 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report in - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:83, position:1423
a rate of one rug for one pizza. 8 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report information within a spatial context. 8.3.1.1.1 Obtain and analyze geograph - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:83, position:1278
countries would be better off if Country A specialized in producing pizzas and Country B specialized in producing rugs and they traded at a rate of one rug for one pizza. 8 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representation - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:83, position:1695
from a variety of print and electronic sources to investigate places or answer specific geographic questions; provide rationale for its use. For example: SourcesŠGeographic Information Systems (GIS), online atlases and databases, Google Earth or - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:84, position:158
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:84, position:237
that... Code Benchmark 8 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report information within a spatial context. 8.3.1.1.2 Create and use various kin - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:84, position:92
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:84, position:583
fiTODALSSfl map basics, as well as points, lines and colored areas to display spatial information. For example: fiTODALSSfl map basicsŠtitle, orientation, date, author, legend key, source, scale. Spatial informationŠcities, roads, boundaries, bodies o - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:84, position:1252
Questions about geographic issues might relate to urban development, environmental concerns, transportation issues, flood control. Geospatial technologyŠGeographic Information Systems (GIS), online atlases and databases, Google Earth or - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:117, position:193
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:117, position:270
that... Code Benchmark 9 10 11 12 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report information within a spatial context. 9.3.1.1.1 Create tables, graphs, char - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:117, position:1157
past and present and plan for the future; provide rationale for using specific technologies for each application. For example: TechnologiesŠaerial photographs, satellite-produced imagery, and geographic information systems (GIS). ApplicationsŠdetermine obstacles that n - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:117, position:128
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:117, position:1189
future; provide rationale for using specific technologies for each application. For example: TechnologiesŠaerial photographs, satellite-produced imagery, and geographic information systems (GIS). ApplicationsŠdetermine obstacles that needed t - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:118, position:307
Skills 2. Geographic Inquiry is a process in which people ask geographic questions and gather, organize and analyze information to solve problems and plan for the future. 9.3.1.2.2 Use geospatial technologies to develop plans for analyzing and - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:118, position:412
and analyze information to solve problems and plan for the future. 9.3.1.2.2 Use geospatial technologies to develop plans for analyzing and solving local and regional problems that have spatial dimensions. For example: Geospatial technology - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:118, position:103
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:118, position:504
geospatial technologies to develop plans for analyzing and solving local and regional problems that have spatial dimensions. For example: Geospatial technologyŠGeographic Information Systems (GIS), online atlases and databases, Google Earth or - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:121, position:489
policies, economic development, and changing cultural values) that shape and change urban and suburban areas in the United States. Use generally accepted models to explain the internal spatial structure of cities in regions in the United St
On this site, 'comparable scores' are calculated as: keywords found divided by total words in the standards document(s) - multiplied by 100,000. The comparable scores attempt to normalize data, accounting for very different sizes of curriculum guidance documentation.
(Comp: 5.549)
(Comp: 0.0)
(Comp: 0.174)
(Comp: 0.0)
(Comp: 0.135)
- Natural Resource and Environmental Service Systems Pathway.pdf, page:12, position:2314
tools, and technologies (e.g., spread of invasive species, movement of wildlife populations, changes to biodiversity of edge of habitat versus interior, etc.). NRES.03.02.02.a. Summarize how GIS can be used to manage, conserve, improve and e - Natural Resource and Environmental Service Systems Pathway.pdf, page:28, position:1322
Demonstrate surveying and cartographic skills to make site measurements in order to address concerns and needs within an ESS situation. NRES.09.01.02.a. Research the methods in which GIS can be used in ESS (e.g., tracing of point pol - Power Structural and Technical Systems Pathway.pdf, page:12, position:833
electrical motor. PST.04.03.07.c. Plan and wire electrical circuits (i.e., single pole switch, three-way switch, duplex outlet, etc.). Minnesota Framework: MN.PST.05. Use control, monitoring, geospatial and other technologies in AFNR power, structural - Power Structural and Technical Systems Pathway.pdf, page:14, position:1441
MN.PST.05.03 Intermediate Course Benchmarks MN.PST.05.03 Advanced Course Benchmarks PST.05.03.01.a. Research and summarize the impact of utilizing geospatial technologies (i.e., GPS, GIS, remote sensing, telematics, etc.) in AFNR sys - Power Structural and Technical Systems Pathway.pdf, page:14, position:186
- Minnesota K-12 Academic Standards in Mathematics 2007 edits May 2022.pdf, page:3, position:989
as shape, size, color and thickness. K Geometry & Measurement Recognize and sort basic two- and three-dimensional shapes; use them to model real-world objects. K.3.1.3 Use basic shapes and spatial reasoning to model objects in the real-world. F
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:4, position:1377
local environments and current times to faraway places and distant times. In addition to learning key concepts, students begin to apply essential disciplinary skills including civics skills, geospatial skills, economic reasoning and historical inquiry - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:5, position:1354
history and government from 1800 to contemporary times. Social studies in the middle grades culminates in the interdisciplinary learning experiences of Global Studies in grade 8. Students apply spatial and chronological perspectives as they study the - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:13, position:128
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:13, position:204
Substrands and Standards Substrand 1: Geospatial Skills Standard 1 People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report information within a spatial context. Standard 2 Geographic inquiry is a p - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:13, position:53
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:18, position:1847
(actions or activities). For example: GoodsŠapple, shirt, toy. ServicesŠhaircut, bus ride, bicycle repair. K 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report info - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:18, position:1923
bus ride, bicycle repair. K 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report information within a spatial context. 0.3.1.1.1 Describe spatial information - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:18, position:1781
between goods (objects that can be seen or touched) and services (actions or activities). For example: GoodsŠapple, shirt, toy. ServicesŠhaircut, bus ride, bicycle repair. K 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:19, position:158
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:19, position:236
that... Code Benchmark K 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report information within a spatial context. 0.3.1.1.2 Describe a map and a globe a - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:19, position:92
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:23, position:158
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:23, position:300
Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report information within a spatial context. 1.3.1.1.1 Create sketch maps to illustrate spatial information about familiar places; describe spat - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:23, position:92
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:23, position:405
report information within a spatial context. 1.3.1.1.1 Create sketch maps to illustrate spatial information about familiar places; describe spatial information found on maps. For example: Spatial informationŠcities, roads, boundaries, bodies - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:27, position:1537
shells used in ancient China, metal coins used in Anatolia (Turkey) in 500 BCE. 2 3. Geography 1. Geospatial SkillsŠThe World in Spatial Terms 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report info - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:27, position:1613
BCE. 2 3. Geography 1. Geospatial SkillsŠThe World in Spatial Terms 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report information within a spatial context. 2.3.1.1.1 Create sketch maps to illust - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:27, position:1443
furs used in Minnesota territory in the early 1800s; salt used in the Roman Empire; cowry shells used in ancient China, metal coins used in Anatolia (Turkey) in 500 BCE. 2 3. Geography 1. Geospatial SkillsŠThe World in Spatial Terms 1. People us - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:27, position:1474
in the early 1800s; salt used in the Roman Empire; cowry shells used in ancient China, metal coins used in Anatolia (Turkey) in 500 BCE. 2 3. Geography 1. Geospatial SkillsŠThe World in Spatial Terms 1. People use geographic representations - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:28, position:187
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:28, position:263
2 3. Geography 1. Geospatial SkillsŠThe World in Spatial Terms 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report information within a spatial context. 2.3.1.1.3 Use maps, photos or other ge - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:28, position:92
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:28, position:124
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:32, position:2129
workers, and machines) required to produce 4.the refrigerators. 3 y 1. People use geographic representations and 3.3.1.1.1 Use maps and concepts of location (relative location aphptialgeospatial technologies to acquire, process and words and c - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:32, position:2266
maps and concepts of location (relative location aphptialgeospatial technologies to acquire, process and words and cardinal and intermediate directions) to Skills report information within a spatial context. describe places in one™s community, the - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:33, position:380
of the United States." Description using intermediate directionsŠfiHawaii is southwest of the continental United States.fl 3 eogaphyr ial Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report in - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:33, position:458
is southwest of the continental United States.fl 3 eogaphyr ial Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report information within a spatial context. 3.3.1.1.2 Create and interpret simple - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:33, position:870
information. 3. G1. GeospatFor example: Global placesŠcountry, continent, ocean. "TODALS" map basicsŠtitle, orientation, date, author, legend (key), and scale. Local placesŠcity, village. Spatial informationŠcities, roads, boundaries, bodies - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:35, position:600
and space. For example: Calendar systemsŠSun dial, Chinese, Hindu, Mayan or Aztec, Hebrew and Islamic calendars, Dakota or Anishinaabe seasonal cycles. Visual representations of location and spatial informationŠChinese "Jingban Tianwen Quantu" m - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:39, position:158
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:39, position:235
Understand that... Code Benchmark 4 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report information within a spatial context. 4.3.1.1.1 Create and use various kind - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:39, position:92
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:40, position:352
people ask geographic questions and gather, organize and analyze information to solve problems and plan for the future. 4.3.1.2.2 Use photographs or satellite-produced images to interpret spatial information about the United States, and also C - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:40, position:92
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:47, position:157
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:47, position:233
Understand that... Code Benchmark 5 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report information within a spatial context. 5.3.1.1.1 Create and use various kinds - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:47, position:92
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:58, position:960
Commission), wildlife preservation (Department of Natural Resources); anti-trust laws to promote competition. 6 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report info - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:58, position:1260
Create and use various kinds of maps, including overlaying thematic maps, of places in Minnesota; incorporate the fiTODALSSfl map basics, as well as points, lines and colored areas to display spatial information. For example: fiTODALSSfl map basics - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:58, position:894
oversight (Securities and Exchange Commission, Federal Trade Commission), wildlife preservation (Department of Natural Resources); anti-trust laws to promote competition. 6 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:58, position:1387
map basics, as well as points, lines and colored areas to display spatial information. For example: fiTODALSSfl map basicsŠtitle, orientation, date, author, legend key, source, and scale. Spatial informationŠcities, roads, boundaries, bodies - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:70, position:920
(Facebook). Undesirable effectsŠPonzi schemes; exploitation of people, the environment, natural resources. 7 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report info - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:70, position:996
environment, natural resources. 7 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report information within a spatial context. 7.3.1.1.1 Create and use various kinds - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:70, position:855
Winfrey, Bill Gates (Microsoft), Martha Stewart, Mark Zuckerberg (Facebook). Undesirable effectsŠPonzi schemes; exploitation of people, the environment, natural resources. 7 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:70, position:1354
map basics, as well as points, lines and colored areas to display spatial information. For example: fiTODALSSfl map basicsŠtitle, orientation, date, author, legend key, source, and scale. Spatial informationŠcities, roads, boundaries, bodies - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:80, position:2267
and Ideas Economic Development and Trade Population and Migration Human Interaction with the Environment Skills such as civic participation, economic reasoning, geographic inquiry and geospatial technology, and historical inquiry Page 81 of - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:83, position:1664
analyze geographic information from a variety of print and electronic sources to investigate places or answer specific geographic questions; provide rationale for its use. For example: SourcesŠGeographic Information Systems (GIS), online atlases and databases, Google Ear - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:83, position:1345
pizzas and Country B specialized in producing rugs and they traded at a rate of one rug for one pizza. 8 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report in - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:83, position:1423
a rate of one rug for one pizza. 8 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report information within a spatial context. 8.3.1.1.1 Obtain and analyze geograph - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:83, position:1278
countries would be better off if Country A specialized in producing pizzas and Country B specialized in producing rugs and they traded at a rate of one rug for one pizza. 8 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representation - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:83, position:1695
from a variety of print and electronic sources to investigate places or answer specific geographic questions; provide rationale for its use. For example: SourcesŠGeographic Information Systems (GIS), online atlases and databases, Google Earth or - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:84, position:158
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:84, position:237
that... Code Benchmark 8 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report information within a spatial context. 8.3.1.1.2 Create and use various kin - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:84, position:92
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:84, position:583
fiTODALSSfl map basics, as well as points, lines and colored areas to display spatial information. For example: fiTODALSSfl map basicsŠtitle, orientation, date, author, legend key, source, scale. Spatial informationŠcities, roads, boundaries, bodies o - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:84, position:1252
Questions about geographic issues might relate to urban development, environmental concerns, transportation issues, flood control. Geospatial technologyŠGeographic Information Systems (GIS), online atlases and databases, Google Earth or - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:117, position:193
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:117, position:270
that... Code Benchmark 9 10 11 12 3. Geography 1. Geospatial Skills 1. People use geographic representations and geospatial technologies to acquire, process and report information within a spatial context. 9.3.1.1.1 Create tables, graphs, char - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:117, position:1157
past and present and plan for the future; provide rationale for using specific technologies for each application. For example: TechnologiesŠaerial photographs, satellite-produced imagery, and geographic information systems (GIS). ApplicationsŠdetermine obstacles that n - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:117, position:128
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:117, position:1189
future; provide rationale for using specific technologies for each application. For example: TechnologiesŠaerial photographs, satellite-produced imagery, and geographic information systems (GIS). ApplicationsŠdetermine obstacles that needed t - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:118, position:307
Skills 2. Geographic Inquiry is a process in which people ask geographic questions and gather, organize and analyze information to solve problems and plan for the future. 9.3.1.2.2 Use geospatial technologies to develop plans for analyzing and - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:118, position:412
and analyze information to solve problems and plan for the future. 9.3.1.2.2 Use geospatial technologies to develop plans for analyzing and solving local and regional problems that have spatial dimensions. For example: Geospatial technology - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:118, position:103
- 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:118, position:504
geospatial technologies to develop plans for analyzing and solving local and regional problems that have spatial dimensions. For example: Geospatial technologyŠGeographic Information Systems (GIS), online atlases and databases, Google Earth or - 2011 Social Studies Standards.pdf, page:121, position:489
policies, economic development, and changing cultural values) that shape and change urban and suburban areas in the United States. Use generally accepted models to explain the internal spatial structure of cities in regions in the United St