GIStandards
https://trbaker.github.io/GIStandards/
A machine analysis of geospatial language in US K-12 state curriculum standards
New Hampshire
Report date: 2021-07-08
The frequency of all keywords found in this state's standards: 17
Comparable state score: 0.336 (median: .303, SD: .324)
The frequency above is the sum of all keywords found in all of this state's four core academic standards and the state's CTE/career standards. This total count is broken down by keyword and discipline area below.
On this site, 'comparable scores' are calculated as: keywords found divided by total words in the standards document(s) - multiplied by 100,000. The comparable scores attempt to normalize data, accounting for very different sizes of curriculum guidance documentation.
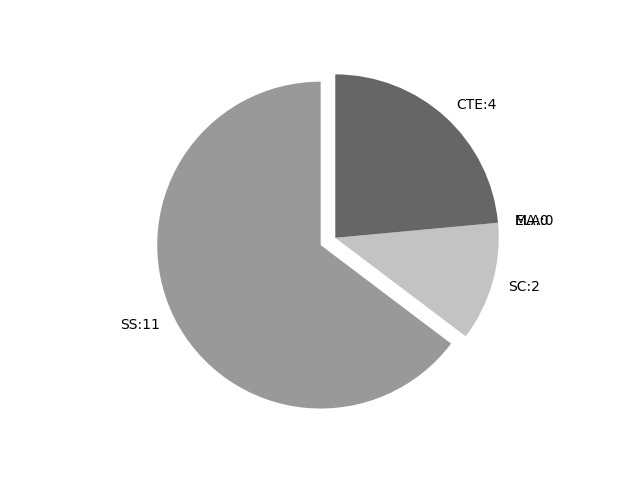
Frequencies by keyword or phrase:Frequencies by discipline area: - SS: 11
(Comp: 2.502) - SC: 2
(Comp: 0.198) - MA: 0
(Comp: 0.0) - ELA: 0
(Comp: 0.0) - CTE: 4
(Comp: 0.112)
Support files: Examples of keyword use by discipline area (and document): - CTE
- pc_ag_es.pdf, page:5, position:2322
facilities, and infrastructure using technology and geospatial techniques (GISGPS). 1 2 3 4 For Example: 29. Demonstrate knowledge of surveying, drafting, remote sensing, and GIS equipment used in planning of tasks in environme - pc_ag_es.pdf, page:5, position:2182
of technological systems critical to the career cluster. ELA: 2,4,6,7,8,9 M: 2,16,17,19 AAI: 5 CRP: 2,4,11 28. Create maps of land, facilities, and infrastructure using technology and geospatial techniques (GISGPS). 1 2 3 4 For Exa - pc_ag_es.pdf, page:5, position:2204
critical to the career cluster. ELA: 2,4,6,7,8,9 M: 2,16,17,19 AAI: 5 CRP: 2,4,11 28. Create maps of land, facilities, and infrastructure using technology and geospatial techniques (GISGPS). 1 2 3 4 For Example: 29. De - pc_ag_es.pdf, page:10, position:2056
56. Create maps of land, facilities, and infrastructure using technological tools. 1 2 3 4 For Example: 57. Demonstrate knowledge of surveying, drafting, remote sensing, and GIS equipment used in planning of tasks in environme
- SC
- standards-science.pdf, page:68, position:787
Assessment does not include the identification and naming of minerals.] MS-ESS2-2. Construct an explanation based on evidence for how geoscience processes have changed at varying time and spatial scales. [Clarification Statement: large (suc - standards-science.pdf, page:97, position:624
Sciences. HS-ESS2 Earth™s Systems Students who demonstrate understanding can: HS-ESS2-1. Develop a model to illustrate how Earth™s internal and surface processes operate at different spatial and temporal scales to form continental and
- SS
- standards-socialstudies-framework.pdf, page:26, position:572
information. SS:GE:2:1.1: Identify the characteristics and purposes of globes and maps. (Themes: C: People, Places and Environment, F: Global Transformation) SS:GE:2:1.2: Introduce spatial information on maps and other geographic repres - standards-socialstudies-framework.pdf, page:26, position:192
- standards-socialstudies-framework.pdf, page:30, position:1793
the effects of migration on the characteristics of places, e.g., cultural awareness or food choices. (Themes: E: Cultural Development, Interaction, and Change) SS:GE:4:4.4: Analyze the spatial patterns of settlement in different regions of t - standards-socialstudies-framework.pdf, page:54, position:1188
e.g., countries through which a person would travel between Cairo and Nairobi. (Themes: C: People, Places and Environment, J: Human Expression and Communication) SS:GE:6:1.2: Apply the spatial concepts of location, distance, direction, scale - standards-socialstudies-framework.pdf, page:54, position:657
between locations of the Earth, recognize complex regional patterns, and appreciate the influence of place on human development. Standard Grades 5-6 Grades 7-8 SS:GE:1: The World in Spatial Terms Students will demonstrate the abilit - standards-socialstudies-framework.pdf, page:58, position:1290
or movement. (Themes: C: People, Places and Environment, E: Cultural Development, Interaction, and Change, I: Patterns of Social and Political Interaction) SS:GE:6:4.4: Analyze the spatial patterns of settlement, e.g., urbanization a - standards-socialstudies-framework.pdf, page:86, position:1437
towards other cultures. (Themes: C: People, Places and Environment, E: Cultural Development, Interaction, and Change, I: Patterns of Social and Political Interaction) SS:GE:12:1.3: Analyze spatial interactions and models of spatial organization, - standards-socialstudies-framework.pdf, page:86, position:649
connections between locations of the Earth, recognize complex regional patterns, and appreciate the influence of place on human development. Standard Grades 9-12 SS:GE:1: The World in Spatial Terms Students will demonstrate the abilit - standards-socialstudies-framework.pdf, page:88, position:1091
systems, e.g., tectonic forces that shape continents and ocean basins. (Themes: C: People, Places and Environment, G: Science, Technology, and Society) SS:GE:12:3.2: Demonstrate the spatial variation in physical processes across Earths su - standards-socialstudies-framework.pdf, page:89, position:1730
consequences of an international debt crisis or the location of oil reserves. (Themes: D: Material Wants and Needs, F: Global Transformation) SS:GE:12:4.4: Classify the functions, sizes, and spatial arrangements of urban areas, e.g., how citie - standards-socialstudies-framework.pdf, page:90, position:1625
e.g., flood plains in New Hampshire or earthquake zones. (Themes: E: Cultural Development, Interaction, and Change, G: Science, Technology, and Society) SS:GE:12:5.4: Examine how the spatial distribution of resources affects patterns of hum
On this site, 'comparable scores' are calculated as: keywords found divided by total words in the standards document(s) - multiplied by 100,000. The comparable scores attempt to normalize data, accounting for very different sizes of curriculum guidance documentation.
(Comp: 2.502)
(Comp: 0.198)
(Comp: 0.0)
(Comp: 0.0)
(Comp: 0.112)
- pc_ag_es.pdf, page:5, position:2322
facilities, and infrastructure using technology and geospatial techniques (GISGPS). 1 2 3 4 For Example: 29. Demonstrate knowledge of surveying, drafting, remote sensing, and GIS equipment used in planning of tasks in environme - pc_ag_es.pdf, page:5, position:2182
of technological systems critical to the career cluster. ELA: 2,4,6,7,8,9 M: 2,16,17,19 AAI: 5 CRP: 2,4,11 28. Create maps of land, facilities, and infrastructure using technology and geospatial techniques (GISGPS). 1 2 3 4 For Exa - pc_ag_es.pdf, page:5, position:2204
critical to the career cluster. ELA: 2,4,6,7,8,9 M: 2,16,17,19 AAI: 5 CRP: 2,4,11 28. Create maps of land, facilities, and infrastructure using technology and geospatial techniques (GISGPS). 1 2 3 4 For Example: 29. De - pc_ag_es.pdf, page:10, position:2056
56. Create maps of land, facilities, and infrastructure using technological tools. 1 2 3 4 For Example: 57. Demonstrate knowledge of surveying, drafting, remote sensing, and GIS equipment used in planning of tasks in environme
- standards-science.pdf, page:68, position:787
Assessment does not include the identification and naming of minerals.] MS-ESS2-2. Construct an explanation based on evidence for how geoscience processes have changed at varying time and spatial scales. [Clarification Statement: large (suc - standards-science.pdf, page:97, position:624
Sciences. HS-ESS2 Earth™s Systems Students who demonstrate understanding can: HS-ESS2-1. Develop a model to illustrate how Earth™s internal and surface processes operate at different spatial and temporal scales to form continental and
- standards-socialstudies-framework.pdf, page:26, position:572
information. SS:GE:2:1.1: Identify the characteristics and purposes of globes and maps. (Themes: C: People, Places and Environment, F: Global Transformation) SS:GE:2:1.2: Introduce spatial information on maps and other geographic repres - standards-socialstudies-framework.pdf, page:26, position:192
- standards-socialstudies-framework.pdf, page:30, position:1793
the effects of migration on the characteristics of places, e.g., cultural awareness or food choices. (Themes: E: Cultural Development, Interaction, and Change) SS:GE:4:4.4: Analyze the spatial patterns of settlement in different regions of t - standards-socialstudies-framework.pdf, page:54, position:1188
e.g., countries through which a person would travel between Cairo and Nairobi. (Themes: C: People, Places and Environment, J: Human Expression and Communication) SS:GE:6:1.2: Apply the spatial concepts of location, distance, direction, scale - standards-socialstudies-framework.pdf, page:54, position:657
between locations of the Earth, recognize complex regional patterns, and appreciate the influence of place on human development. Standard Grades 5-6 Grades 7-8 SS:GE:1: The World in Spatial Terms Students will demonstrate the abilit - standards-socialstudies-framework.pdf, page:58, position:1290
or movement. (Themes: C: People, Places and Environment, E: Cultural Development, Interaction, and Change, I: Patterns of Social and Political Interaction) SS:GE:6:4.4: Analyze the spatial patterns of settlement, e.g., urbanization a - standards-socialstudies-framework.pdf, page:86, position:1437
towards other cultures. (Themes: C: People, Places and Environment, E: Cultural Development, Interaction, and Change, I: Patterns of Social and Political Interaction) SS:GE:12:1.3: Analyze spatial interactions and models of spatial organization, - standards-socialstudies-framework.pdf, page:86, position:649
connections between locations of the Earth, recognize complex regional patterns, and appreciate the influence of place on human development. Standard Grades 9-12 SS:GE:1: The World in Spatial Terms Students will demonstrate the abilit - standards-socialstudies-framework.pdf, page:88, position:1091
systems, e.g., tectonic forces that shape continents and ocean basins. (Themes: C: People, Places and Environment, G: Science, Technology, and Society) SS:GE:12:3.2: Demonstrate the spatial variation in physical processes across Earths su - standards-socialstudies-framework.pdf, page:89, position:1730
consequences of an international debt crisis or the location of oil reserves. (Themes: D: Material Wants and Needs, F: Global Transformation) SS:GE:12:4.4: Classify the functions, sizes, and spatial arrangements of urban areas, e.g., how citie - standards-socialstudies-framework.pdf, page:90, position:1625
e.g., flood plains in New Hampshire or earthquake zones. (Themes: E: Cultural Development, Interaction, and Change, G: Science, Technology, and Society) SS:GE:12:5.4: Examine how the spatial distribution of resources affects patterns of hum