GIStandards
https://trbaker.github.io/GIStandards/
A machine analysis of geospatial language in US K-12 state curriculum standards
Oklahoma
Report date: 2021-07-08
The frequency of all keywords found in this state's standards: 11
Comparable state score: 0.389 (median: .303, SD: .324)
The frequency above is the sum of all keywords found in all of this state's four core academic standards and the state's CTE/career standards. This total count is broken down by keyword and discipline area below.
On this site, 'comparable scores' are calculated as: keywords found divided by total words in the standards document(s) - multiplied by 100,000. The comparable scores attempt to normalize data, accounting for very different sizes of curriculum guidance documentation.
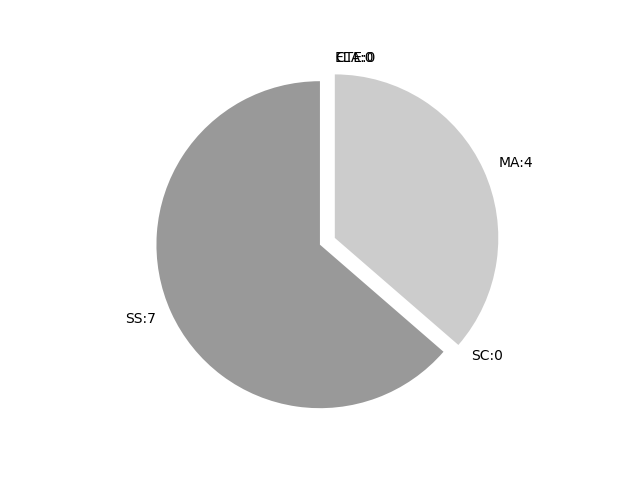
Frequencies by keyword or phrase:Frequencies by discipline area: - SS: 7
(Comp: 1.076) - SC: 0
(Comp: 0.0) - MA: 4
(Comp: 0.443) - ELA: 0
(Comp: None) - CTE: 0
(Comp: None)
Support files: Examples of keyword use by discipline area (and document): - MA
- OAS-Math-Final Version_3.pdf, page:4, position:2340
in their daily lives. A focus on geometry should enable students to analyze characteristics of two- and three-dimensional objects, develop arguments based on geometric relationships, describe spatial relationships using coordinate geometry and oth - OAS-Math-Final Version_3.pdf, page:11, position:1128
interchangeably. K.GM.1.4 Use smaller shapes to form a larger shape when there is an outline to follow. K.GM.1.5 Compose free-form shapes with blocks. K.GM.1.6 Use basic shapes and spatial reasoning to represent objects in the real world. - OAS-Math-Final Version_3.pdf, page:53, position:263
A Page A.11 Slope (of a line) A measure of the steepness of a line in a Cartesian plane, found by determining the constant change in the !-coordinate per 1-unit change in the !-coordinate. Spatial sense The ability to build and manipulate mental - OAS-Math-Final Version_3.pdf, page:59, position:922
interchangeably. K.GM.1.4 Use smaller shapes to form a larger shape when there is an outline to follow. K.GM.1.5 Compose free-form shapes with blocks. K.GM.1.6 Use basic shapes and spatial reasoning to represent objects in the real world
- SS
- Oklahoma Academic Standards for Social Studies 8.26.19.pdf, page:17, position:1686
of the United States. 4.2.1 Use maps and other geographic representations (such as globes and graphs), tools, and technologies to acquire, process, and report information from a spatial perspective. A. Use and describe various ele - Oklahoma Academic Standards for Social Studies 8.26.19.pdf, page:24, position:896
direction, relative location, absolute location, and latitude and longitude. 6.1.3 Integrate visual information, draw conclusions, and make predictions from geographic data and analyze spatial distribution and patterns by interpreting that d - Oklahoma Academic Standards for Social Studies 8.26.19.pdf, page:27, position:1201
and physical features of the about people, places, and environments. 7.1.5 Integrate visual information, draw conclusions, and make predictions from geographic data; analyze spatial distribution and patterns by interpreting that d - Oklahoma Academic Standards for Social Studies 8.26.19.pdf, page:62, position:1030
WG.1.3 Define regions and evaluate the regionalization process to characterize and analyze changing interconnections among places. WG.1.4 Utilize geographic technologies of GIS, remote sensing and GPS sources of geographical d - Oklahoma Academic Standards for Social Studies 8.26.19.pdf, page:62, position:523
Human Geography Content Standards WG.1 The student will use maps and other geographic representations, tools and technologies to acquire, research, process, and solve problems from a spatial perspective. WG.1.1 Analyze key con - Oklahoma Academic Standards for Social Studies 8.26.19.pdf, page:79, position:1241
describe the physical and human features of the community and state. 3.B.4-5.2 Create and use maps, data graphs and charts, photographs, and other geographic representations to explain spatial relationships of physical and human places. - Oklahoma Academic Standards for Social Studies 8.26.19.pdf, page:80, position:1091
and how people and goods move from place to place. 3.B.2-3.6 Describe how the movement of resources, people, goods, and ideas move, connecting communities. 3.B.4-5.6 Describe the spatial patterns of economic activities caused by inte
On this site, 'comparable scores' are calculated as: keywords found divided by total words in the standards document(s) - multiplied by 100,000. The comparable scores attempt to normalize data, accounting for very different sizes of curriculum guidance documentation.
(Comp: 1.076)
(Comp: 0.0)
(Comp: 0.443)
(Comp: None)
(Comp: None)
- OAS-Math-Final Version_3.pdf, page:4, position:2340
in their daily lives. A focus on geometry should enable students to analyze characteristics of two- and three-dimensional objects, develop arguments based on geometric relationships, describe spatial relationships using coordinate geometry and oth - OAS-Math-Final Version_3.pdf, page:11, position:1128
interchangeably. K.GM.1.4 Use smaller shapes to form a larger shape when there is an outline to follow. K.GM.1.5 Compose free-form shapes with blocks. K.GM.1.6 Use basic shapes and spatial reasoning to represent objects in the real world. - OAS-Math-Final Version_3.pdf, page:53, position:263
A Page A.11 Slope (of a line) A measure of the steepness of a line in a Cartesian plane, found by determining the constant change in the !-coordinate per 1-unit change in the !-coordinate. Spatial sense The ability to build and manipulate mental - OAS-Math-Final Version_3.pdf, page:59, position:922
interchangeably. K.GM.1.4 Use smaller shapes to form a larger shape when there is an outline to follow. K.GM.1.5 Compose free-form shapes with blocks. K.GM.1.6 Use basic shapes and spatial reasoning to represent objects in the real world
- Oklahoma Academic Standards for Social Studies 8.26.19.pdf, page:17, position:1686
of the United States. 4.2.1 Use maps and other geographic representations (such as globes and graphs), tools, and technologies to acquire, process, and report information from a spatial perspective. A. Use and describe various ele - Oklahoma Academic Standards for Social Studies 8.26.19.pdf, page:24, position:896
direction, relative location, absolute location, and latitude and longitude. 6.1.3 Integrate visual information, draw conclusions, and make predictions from geographic data and analyze spatial distribution and patterns by interpreting that d - Oklahoma Academic Standards for Social Studies 8.26.19.pdf, page:27, position:1201
and physical features of the about people, places, and environments. 7.1.5 Integrate visual information, draw conclusions, and make predictions from geographic data; analyze spatial distribution and patterns by interpreting that d - Oklahoma Academic Standards for Social Studies 8.26.19.pdf, page:62, position:1030
WG.1.3 Define regions and evaluate the regionalization process to characterize and analyze changing interconnections among places. WG.1.4 Utilize geographic technologies of GIS, remote sensing and GPS sources of geographical d - Oklahoma Academic Standards for Social Studies 8.26.19.pdf, page:62, position:523
Human Geography Content Standards WG.1 The student will use maps and other geographic representations, tools and technologies to acquire, research, process, and solve problems from a spatial perspective. WG.1.1 Analyze key con - Oklahoma Academic Standards for Social Studies 8.26.19.pdf, page:79, position:1241
describe the physical and human features of the community and state. 3.B.4-5.2 Create and use maps, data graphs and charts, photographs, and other geographic representations to explain spatial relationships of physical and human places. - Oklahoma Academic Standards for Social Studies 8.26.19.pdf, page:80, position:1091
and how people and goods move from place to place. 3.B.2-3.6 Describe how the movement of resources, people, goods, and ideas move, connecting communities. 3.B.4-5.6 Describe the spatial patterns of economic activities caused by inte